Periodic Table Element Comparison: Compare Elements - Boron vs Nitrogen
Compare Boron and Nitrogen on the basis of their properties, attributes and periodic table facts. Compare elements on more than 90 properties. All the elements of similar categories show a lot of similarities and differences in their chemical, atomic, physical properties and uses. These similarities and dissimilarities should be known while we study periodic table elements. You can study the detailed comparison between Boron vs Nitrogen with most reliable information about their properties, attributes, facts, uses etc. You can compare B vs N on more than 90 properties like electronegativity , oxidation state, atomic shells, orbital structure, Electronaffinity, physical states, electrical conductivity and many more. Boron and Nitrogen comparison table on more than 90 properties.
Boron and Nitrogen Comparison
Facts
| Name | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 5 | 7 |
| Atomic Symbol | B | N |
| Atomic Weight | 10.811 | 14.0067 |
| Phase at STP | Solid | Gas |
| Color | Black | Colorless |
| Metallic Classification | Metalloid | Other Nonmetal |
| Group in Periodic Table | group 13 | group 15 |
| Group Name | boron family | nitrogen family |
| Period in Periodic Table | period 2 | period 2 |
| Block in Periodic Table | p -block | p -block |
| Electronic Configuration | [He] 2s2 2p1 | [He] 2s2 2p3 |
| Electronic Shell Structure (Electrons per shell) | 2, 3 | 2, 5 |
| Melting Point | 2348 K | 63.05 K |
| Boiling Point | 4273 K | 77.36 K |
| CAS Number | CAS7440-42-8 | CAS7727-37-9 |
| Neighborhood Elements | Neighborhood Elements of Boron | Neighborhood Elements of Nitrogen |
History
| Parameter | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| History | The element Boron was discovered by L. Gay-Lussac and L.J. Thénard in year 1808 in France and United Kingdom. Boron derived its name from borax, a mineral. | The element Nitrogen was discovered by D. Rutherford in year 1772 in United Kingdom. Nitrogen derived its name from the Greek word nitron and '-gen' meaning 'niter-forming'. |
| Discovery | L. Gay-Lussac and L.J. Thénard (1808) | D. Rutherford (1772) |
| Isolated | H. Davy (1808) | D. Rutherford (1772) |
Presence: Abundance in Nature and Around Us
Parts per billion (ppb) by weight / by atoms (1ppb =10^-7 %)
| Property | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Abundance in Universe | 1 / 0.1 | 1000000 / 90000 |
| Abundance in Sun | 2 / 0.2 | 1000000 / 90000 |
| Abundance in Meteorites | 1600 / 3000 | 1400000 / 1400000 |
| Abundance in Earth's Crust | 8700 / 17000 | 20000 / 29000 |
| Abundance in Oceans | 4440 / 2500 | 500 / 220 |
| Abundance in Humans | 700 / 410 | 26000000 / 12000000 |
Crystal Structure and Atomic Structure
| Property | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Volume | 4.3947 cm3/mol | 22.4131 cm3/mol |
| Atomic Radius | 87 pm | 56 pm |
| Covalent Radius | 82 pm | 75 pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 192 pm | 155 pm |
Atomic Spectrum - Spectral Lines | ||
| Emission Spectrum | Not available |  |
| Absorption Spectrum |  |  |
| Lattice Constant | 506, 506, 506 pm | 386.1, 386.1, 626.5 pm |
| Lattice Angle | 1.01334, 1.01334, 1.01334 | π/2, π/2, 2 π/3 |
| Space Group Name | R_ 3m | P63/mmc |
| Space Group Number | 166 | 194 |
| Crystal Structure | Simple Trigonal 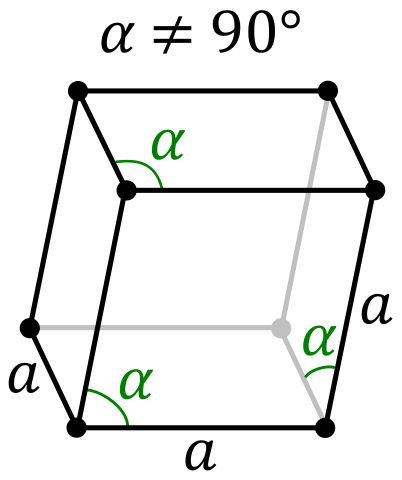 | Simple Hexagonal 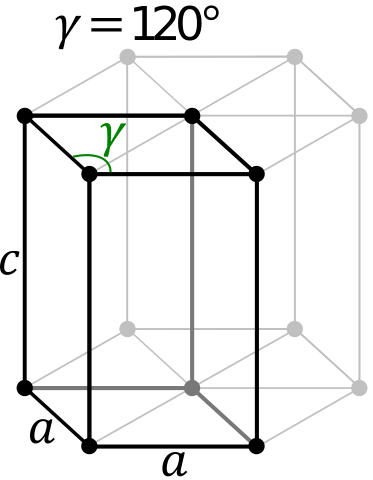 |
Atomic and Orbital Properties
| Property | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 5 | 7 |
| Number of Electrons (with no charge) | 5 | 7 |
| Number of Protons | 5 | 7 |
| Mass Number | 10.811 | 14.0067 |
| Number of Neutrons | 6 | 7 |
| Shell structure (Electrons per energy level) | 2, 3 | 2, 5 |
| Electron Configuration | [He] 2s2 2p1 | [He] 2s2 2p3 |
| Valence Electrons | 2s2 2p1 | 2s2 2p3 |
| Oxidation State | 3 | -3, 3, 5 |
| Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) | 2P1/2 | 4S3/2 |
| Shell structure | 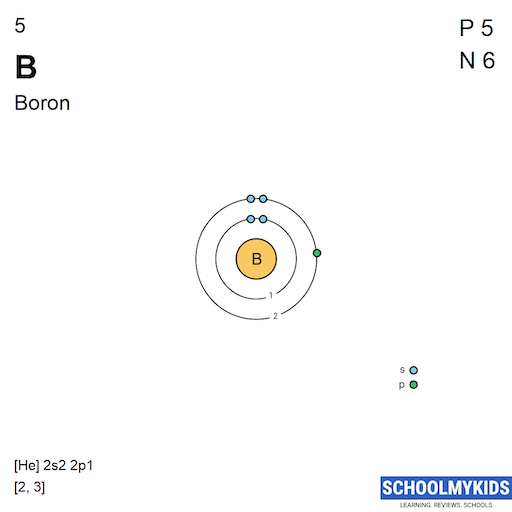 | 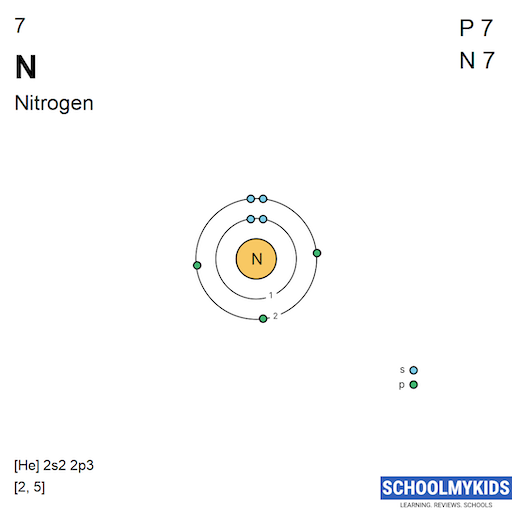 |
Isotopes and Nuclear Properties
Boron has 2 stable naturally occuring isotopes while Nitrogen has 2 stable naturally occuring isotopes.
| Parameter | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Known Isotopes | 6B, 7B, 8B, 9B, 10B, 11B, 12B, 13B, 14B, 15B, 16B, 17B, 18B, 19B | 10N, 11N, 12N, 13N, 14N, 15N, 16N, 17N, 18N, 19N, 20N, 21N, 22N, 23N, 24N, 25N |
| Stable Isotopes | Naturally occurring stable isotopes: 10B, 11B | Naturally occurring stable isotopes: 14N, 15N |
| Neutron Cross Section | 755 | 1.91 |
| Neutron Mass Absorption | 2.4 | 0.0048 |
Chemical Properties: Ionization Energies and electron affinity
| Property | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Valence or Valency | 3 | 3 |
| Electronegativity | 2.04 Pauling Scale | 3.04 Pauling Scale |
| Electron Affinity | 26.7 kJ/mol | 7 kJ/mol |
| Ionization Energies | 1st: 800.6 kJ/mol 2nd: 2427.1 kJ/mol 3rd: 3659.7 kJ/mol 4th: 25025.8 kJ/mol 5th: 32826.7 kJ/mol | 1st: 1402.3 kJ/mol 2nd: 2856 kJ/mol 3rd: 4578.1 kJ/mol 4th: 7475 kJ/mol 5th: 9444.9 kJ/mol 6th: 53266.6 kJ/mol 7th: 64360 kJ/mol |
Physical Properties
| Property | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.46 g/cm3 | 0.001251 g/cm3 |
| Molar Volume | 4.3947 cm3/mol | 22.4131 cm3/mol |
Elastic Properties | ||
| Young Modulus | - | - |
| Shear Modulus | - | - |
| Bulk Modulus | 320 GPa | - |
| Poisson Ratio | - | - |
Hardness - Tests to Measure of Hardness of Element | ||
| Mohs Hardness | 9.3 MPa | - |
| Vickers Hardness | 49000 MPa | - |
| Brinell Hardness | - | - |
Electrical Properties | ||
| Electrical Conductivity | 0.0001 S/m | - |
| Resistivity | 10000 m Ω | - |
| Superconducting Point | - | - |
Heat and Conduction Properties | ||
| Thermal Conductivity | 27 W/(m K) | 0.02583 W/(m K) |
| Thermal Expansion | 0.000006 /K | - |
Magnetic Properties | ||
| Magnetic Type | Diamagnetic | Diamagnetic |
| Curie Point | - | - |
| Mass Magnetic Susceptibility | -8.7e-9 m3/kg | -5.4e-9 m3/kg |
| Molar Magnetic Susceptibility | -9.41e-11 m3/mol | -1.5e-10 m3/mol |
| Volume Magnetic Susceptibility | -0.0000214 | -6.8e-9 |
Optical Properties | ||
| Refractive Index | - | 1.000298 |
Acoustic Properties | ||
| Speed of Sound | 16200 m/s | 333.6 m/s |
Thermal Properties - Enthalpies and thermodynamics
| Property | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 2348 K | 63.05 K |
| Boiling Point | 4273 K | 77.36 K |
| Critical Temperature | - | 126.21 K |
| Superconducting Point | - | - |
Enthalpies | ||
| Heat of Fusion | 50 kJ/mol | 0.36 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 507 kJ/mol | 2.79 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Combustion | - | - |
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
| Parameter | Boron | Nitrogen |
|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | CAS7440-42-8 | CAS7727-37-9 |
| RTECS Number | RTECSED7350000 | RTECSQW9700000 |
| DOT Hazard Class | - | 2.2 |
| DOT Numbers | - | 1977 |
| EU Number | - | - |
| NFPA Fire Rating | 3 | 0 |
| NFPA Health Rating | 2 | 3 |
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 0 | 0 |
| NFPA Hazards | - | - |
| AutoIgnition Point | - | - |
| Flashpoint | - | - |
Compare With Other Elements
Compare Boron and Nitrogen with other elements of the periodic table.
Compare Boron with all Group 13 elementsCompare Boron with AluminiumCompare Boron with GalliumCompare Boron with IndiumCompare Boron with ThalliumCompare Boron with Nihonium Compare Boron with all Period 2 elementsCompare Boron with LithiumCompare Boron with BerylliumCompare Boron with CarbonCompare Boron with NitrogenCompare Boron with OxygenCompare Boron with FluorineCompare Boron with Neon Compare Boron with all Metalloid elements | Compare Nitrogen with all Group 15 elementsNitrogen vs Phosphorus ComparisonNitrogen vs Arsenic ComparisonNitrogen vs Antimony ComparisonNitrogen vs Bismuth ComparisonNitrogen vs Moscovium Comparison Compare Nitrogen with all Period 2 elementsNitrogen vs Lithium ComparisonNitrogen vs Beryllium ComparisonNitrogen vs Boron ComparisonNitrogen vs Carbon ComparisonNitrogen vs Oxygen ComparisonNitrogen vs Fluorine ComparisonNitrogen vs Neon Comparison Compare Nitrogen with all Other Nonmetal elements |

