Osmium Element Information, Facts, Properties, Trends, Uses, Comparison with other elements

In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn about Osmium's unique chemical and physical properties, trends in the periodic table, isotopes, and its historical significance. We'll also cover its abundance, crystal structure, electron configuration, and health & safety guidelines. Explore how Osmium compares with other elements and discover its many uses.
Osmium (from Greek osme (ὀσμή) meaning 'smell') is a chemical element with symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white Transition Metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, mostly in platinum ores. Osmium is the densest naturally occurring element, with a density of 7004225900000000000♠22.59 g/cm3.
It belongs to group 8 of the periodic table having trivial name null. You can also download Printable Periodic Table of Elements Flashcards for Osmium in a PDF format.
Osmium Facts
Read key information and facts about element Osmium
| Name | Osmium |
| Atomic Number | 76 |
| Atomic Symbol | Os |
| Atomic Weight | 190.23 |
| Phase | Solid |
| Color | SlateGray |
| Appearance | silvery, blue cast |
| Classification | Transition Metal |
| Natural Occurance | Primordial |
| Group in Periodic Table | 8 |
| Group Name | iron family |
| Period in Periodic Table | period 6 |
| Block in Periodic Table | d-block |
| Electronic Configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2 |
| Electronic Shell Structure (Electrons per shell) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2 |
| Melting Point | 3306 K |
| Boiling Point | 5285 K |
| CAS Number | CAS7440-04-2 |
How to Locate Osmium on Periodic Table
Periodic table is arranged by atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus which is same as number of electrons. The atomic number increases from left to right. Periodic table starts at top left ( Atomic number 1) and ends at bottom right (atomic number 118). Therefore you can directly look for atomic number 76 to find Osmium on periodic table.
Another way to read periodic table and locate an element is by using group number (column) and period number (row). To locate Osmium on periodic table look for cross section of group 8 and period 6 in the modern periodic table.
Osmium History
The element Osmium was discovered by S. Tennant in year 1803 in United Kingdom. Osmium was first isolated by S. Tennant in 1803. Osmium derived its name from the Greek osmè, meaning 'smell'.
| Discovered By | S. Tennant |
| Discovery Date | 1803 in United Kingdom |
| First Isolation | 1803 |
| Isolated by | S. Tennant |
Tennant had been working on samples of South American platinum in parallel with Wollaston and discovered two new elements, which he named osmium and iridium.
Osmium Uses
The element Osmium has Osmium is mainly used to make tough metal alloys. You can find it in ballpoint pen tips, record needles, electrical contacts, and other metal components where friction needs to be reduced.. Since element Osmium has extremely short half-lives
Osmium Presence: Abundance in Nature and Around Us
The table below shows the abundance of Osmium in Universe, Sun, Meteorites, Earth's Crust, Oceans and Human Body.
| ppb by weight (1ppb =10^-7 %) | ppb by atoms (1ppb =10^-7 %) | |
|---|---|---|
| Abundance in Universe | 3 | 0.02 |
| Abundance in Sun | 2 | 0.02 |
| Abundance in Meteorites | 670 | 70 |
| Abundance in Earth's Crust | 1.8 | 0.2 |
| Abundance in Oceans | - | - |
| Abundance in Humans | - | - |
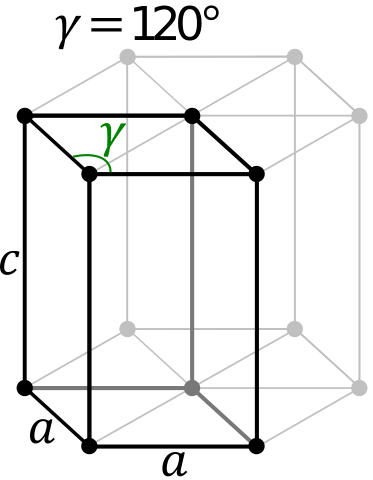
Crystal Structure of Osmium
The solid state structure of Osmium is Simple Hexagonal.
The Crystal structure can be described in terms of its unit Cell. The unit Cells repeats itself in three dimensional space to form the structure.
Unit Cell Parameters
The unit cell is represented in terms of its lattice parameters, which are the lengths of the cell edges Lattice Constants (a, b and c)
| a | b | c |
|---|---|---|
| 273.44 pm | 273.44 pm | 431.73 pm |
and the angles between them Lattice Angles (alpha, beta and gamma).
| alpha | beta | gamma |
|---|---|---|
| π/2 | π/2 | 2 π/3 |
The positions of the atoms inside the unit cell are described by the set of atomic positions ( xi, yi, zi) measured from a reference lattice point.
The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space are described by the 230 space groups (219 distinct types, or 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct.
| Space Group Name | P63/mmc |
| Space Group Number | 194 |
| Crystal Structure | Simple Hexagonal |
| Number of atoms per unit cell |
The number of atoms per unit cell in a simple cubic, face-centered cubic and body-centred cubic are 1,4,2 respectively.
Osmium Atomic and Orbital Properties
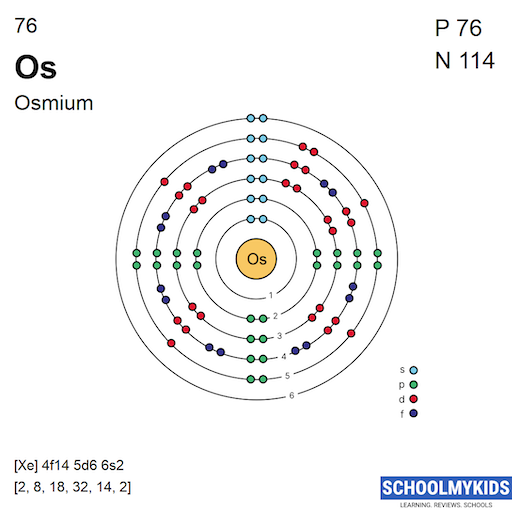
Osmium atoms have 76 electrons and the electronic shell structure is [2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) 5D4.
| Atomic Number | 76 |
| Number of Electrons (with no charge) | 76 |
| Number of Protons | 76 |
| Mass Number | 190 |
| Number of Neutrons | 114 |
| Shell structure (Electrons per energy level) | 2, 8, 18, 32, 14, 2 |
| Electron Configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2 |
| Valence Electrons | 5d6 6s2 |
| Valence (Valency) | 6 |
| Main Oxidation States | 4 |
| Oxidation States | -4, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 |
| Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) | 5D4 |
Bohr Atomic Model of Osmium - Electrons per energy level
| n | s | p | d | f |
|---|
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Osmium - neutral Osmium atom
Abbreviated electronic configuration of Osmium
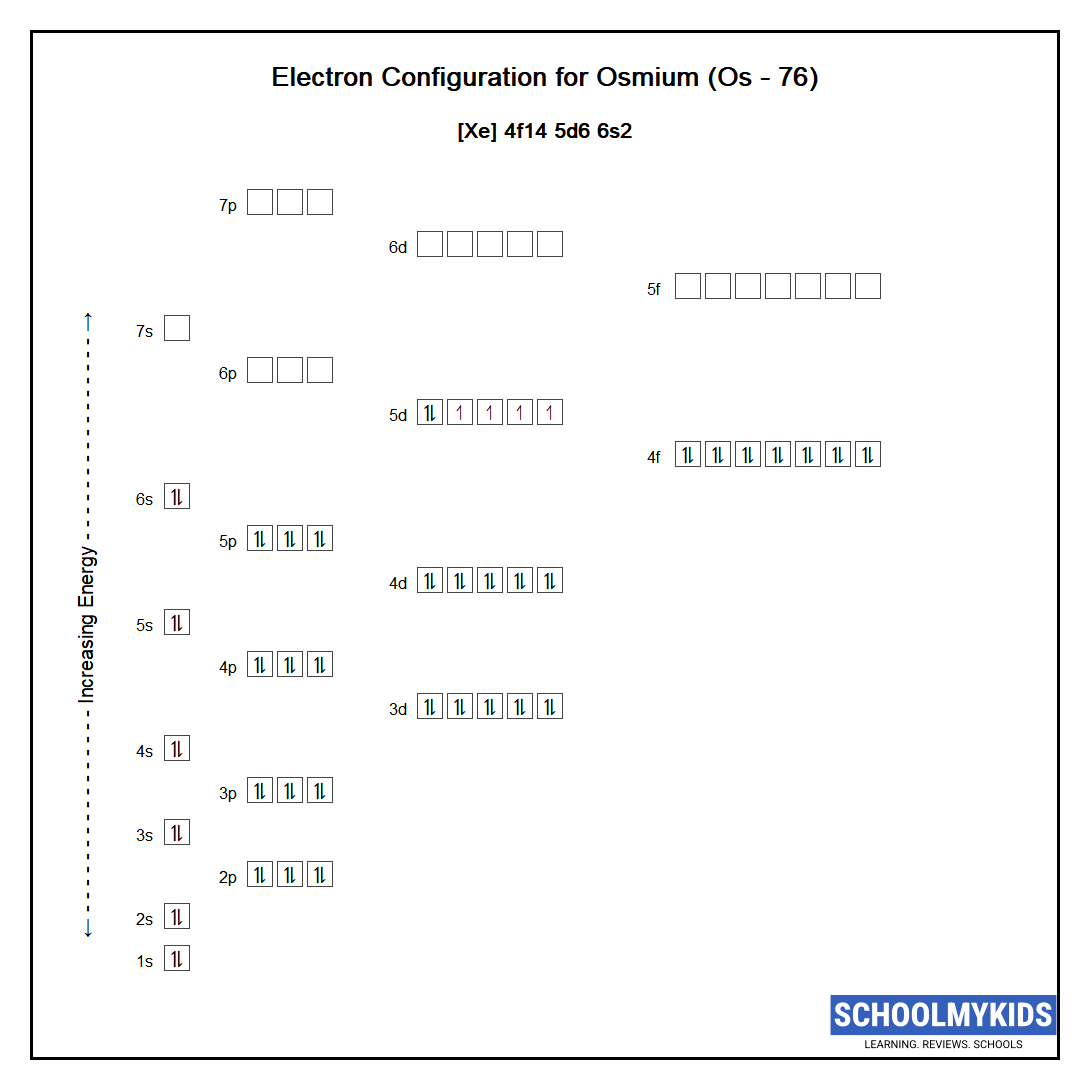
The ground state abbreviated electronic configuration of Neutral Osmium atom is [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2. The portion of Osmium configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, is abbreviated as [Xe]. For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. This is important as it is the Valence electrons 5d6 6s2, electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemical properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Osmium
Complete ground state electronic configuration for the Osmium atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 4f14 5d6 6s2
Electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the order determined by the Aufbau principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule.
As per the Aufbau principle the electrons will occupy the orbitals having lower energies before occupying higher energy orbitals. According to this principle, electrons are filled in the following order: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p…
The Pauli exclusion principle states that a maximum of two electrons, each having opposite spins, can fit in an orbital.
Hund's rule states that every orbital in a given subshell is singly occupied by electrons before a second electron is filled in an orbital.
Atomic Structure of Osmium
Osmium atomic radius is 185 pm, while it's covalent radius is 128 pm.
| Atomic Radius Calculated | 185 pm(1.85 Å) |
| Atomic Radius Empirical | 130 pm (1.3 Å) |
| Atomic Volume | 8.421 cm3/mol |
| Covalent Radius | 128 pm (1.28 Å) |
| Van der Waals Radius | - |
| Neutron Cross Section | 15 |
| Neutron Mass Absorption | 0.0023 |
Spectral Lines of Osmium - Atomic Spectrum of Osmium
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from an excess or deficiency of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules.
Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a quantum system and a single photon. A spectral line may be observed either as an emission line or an absorption line.
Spectral lines are highly atom-specific, and can be used to identify the chemical composition of any medium. Several elements, including helium, thallium, and caesium, were discovered by spectroscopic means. They are widely used to determine the physical conditions of stars and other celestial bodies that cannot be analyzed by other means.
Emission spectrum of Osmium

Absorption spectrum of Osmium

Osmium Chemical Properties: Osmium Ionization Energies and electron affinity
The electron affinity of Osmium is 106.1 kJ/mol.
| Valence | 6 |
| Electronegativity | 2.2 |
| ElectronAffinity | 106.1 kJ/mol |
Ionization Energy of Osmium
Ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or molecule.in chemistry, this energy is expresed in kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol) or kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol).
Refer to table below for Ionization energies of Osmium
Here are the ionization energies of Osmium (Os) both in electron volts (eV) and in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol).
| Ionization energy number | Enthalpy in kJ/mol | Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 840 | 8.706 |
| 2nd | 1600 | 16.583 |
The conversion from kJ/mol to eV is done using the formula:
Energy (kJ/mol) = Energy (eV) x 96.485 Energy (kJ/mol)=Energy (eV)x96.485
where 1 eV = 96.485 kJ/mol.
1 electronvolt (eV) is equal to 96.485 kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol)
Osmium Physical Properties
Refer to below table for Osmium Physical Properties
| Density | 22.59 g/cm3(when liquid at m.p density is $20 g/cm3) |
| Molar Volume | 8.421 cm3/mol |
Elastic Properties
| Young Modulus | - |
| Shear Modulus | 222 GPa |
| Bulk Modulus | - |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.25 |
Hardness of Osmium - Tests to Measure of Hardness of Element
| Mohs Hardness | 7 MPa |
| Vickers Hardness | - |
| Brinell Hardness | 3920 MPa |
Osmium Electrical Properties
Electrical resistivity measures element's electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current.The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-metre (Ω⋅m). While Electrical conductivity is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a element's ability to conduct electric current. The SI unit of electrical conductivity is siemens per metre (S/m).
Osmium is a conductor of electricity. Refer to table below for the Electrical properties of Osmium
| Electrical conductors | Conductor |
| Electrical Conductivity | 12000000 S/m |
| Resistivity | 8.1e-8 m Ω |
| Superconducting Point | 0.66 |
Osmium Heat and Conduction Properties
| Thermal Conductivity | 88 W/(m K) |
| Thermal Expansion | 0.0000051 /K |
Osmium Magnetic Properties
| Magnetic Type | Paramagnetic |
| Curie Point | - |
| Mass Magnetic Susceptibility | 6e-10 m3/kg |
| Molar Magnetic Susceptibility | 1.1e-10 m3/mol |
| Volume Magnetic Susceptibility | 0.000014 |
Optical Properties of Osmium
| Refractive Index | - |
Acoustic Properties of Osmium
| Speed of Sound | 4940 m/s |
Osmium Thermal Properties - Enthalpies and thermodynamics
Refer to table below for Thermal properties of Osmium
| Melting Point | 3306 K(3032.85 °C, 5491.130 °F) |
| Boiling Point | 5285 K(5011.85 °C, 9053.330 °F) |
| Critical Temperature | - |
| Superconducting Point | 0.66 |
Enthalpies of Osmium
| Heat of Fusion | 31 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Vaporization | 630 kJ/mol |
| Heat of Combustion | - |
Osmium Isotopes - Nuclear Properties of Osmium
Osmium has 35 isotopes, with between 162 and 196 nucleons. Osmium has 6 stable naturally occuring isotopes.
Isotopes of Osmium - Naturally occurring stable Isotopes: 184Os, 187Os, 188Os, 189Os, 190Os, 192Os.
| Isotope | Z | N | Isotope Mass | % Abundance | T half | Decay Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 162Os | 76 | 86 | 162 | Synthetic | ||
| 163Os | 76 | 87 | 163 | Synthetic | ||
| 164Os | 76 | 88 | 164 | Synthetic | ||
| 165Os | 76 | 89 | 165 | Synthetic | ||
| 166Os | 76 | 90 | 166 | Synthetic | ||
| 167Os | 76 | 91 | 167 | Synthetic | ||
| 168Os | 76 | 92 | 168 | Synthetic | ||
| 169Os | 76 | 93 | 169 | Synthetic | ||
| 170Os | 76 | 94 | 170 | Synthetic | ||
| 171Os | 76 | 95 | 171 | Synthetic | ||
| 172Os | 76 | 96 | 172 | Synthetic | ||
| 173Os | 76 | 97 | 173 | Synthetic | ||
| 174Os | 76 | 98 | 174 | Synthetic | ||
| 175Os | 76 | 99 | 175 | Synthetic | ||
| 176Os | 76 | 100 | 176 | Synthetic | ||
| 177Os | 76 | 101 | 177 | Synthetic | ||
| 178Os | 76 | 102 | 178 | Synthetic | ||
| 179Os | 76 | 103 | 179 | Synthetic | ||
| 180Os | 76 | 104 | 180 | Synthetic | ||
| 181Os | 76 | 105 | 181 | Synthetic | ||
| 182Os | 76 | 106 | 182 | Synthetic | ||
| 183Os | 76 | 107 | 183 | Synthetic | ||
| 184Os | 76 | 108 | 184 | 0.02% | Stable | N/A |
| 185Os | 76 | 109 | 185 | Synthetic | ||
| 186Os | 76 | 110 | 186 | 1.59% | Stable | N/A |
| 187Os | 76 | 111 | 187 | 1.96% | Stable | N/A |
| 188Os | 76 | 112 | 188 | 13.24% | Stable | N/A |
| 189Os | 76 | 113 | 189 | 16.15% | Stable | N/A |
| 190Os | 76 | 114 | 190 | 26.26% | Stable | |
| 191Os | 76 | 115 | 191 | Synthetic | ||
| 192Os | 76 | 116 | 192 | 40.78% | Stable | N/A |
| 193Os | 76 | 117 | 193 | Synthetic | ||
| 194Os | 76 | 118 | 194 | Synthetic | ||
| 195Os | 76 | 119 | 195 | Synthetic | ||
| 196Os | 76 | 120 | 196 | Synthetic |
Regulatory and Health - Health and Safety Parameters and Guidelines
The United States Department of Transportation (DOT) identifies hazard class of all dangerous elements/goods/commodities either by its class (or division) number or name. The DOT has divided these materials into nine different categories, known as Hazard Classes.
| DOT Numbers | 3089 |
| DOT Hazard Class | 4.1 |
NFPA 704 is a Standard System for the Identification of the Hazards of Materials for Emergency Response. NFPA is a standard maintained by the US based National Fire Protection Association.
The health (blue), flammability (red), and reactivity (yellow) rating all use a numbering scale ranging from 0 to 4. A value of zero means that the element poses no hazard; a rating of four indicates extreme danger.
| NFPA Fire Rating | 4 | Flash Points below 22.8°C (73°F) |
| NFPA Health Rating | ||
| NFPA Reactivity Rating | 1 | Flash Points Above 93.3°C (200°F) |
| NFPA Hazards |
| Autoignition Point | - |
| Flashpoint | - |
Database Search
List of unique identifiers to search the element in various chemical registry databases
| Database | Identifier number |
|---|---|
| CAS Number - Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) | CAS7440-04-2 |
| RTECS Number | RTECSRN1100000 |
| CID Number | CID23937 |
| Gmelin Number | - |
| NSC Number | - |
Compare Osmium with other elements
Compare Osmium with Group 8, Period 6 and Transition Metal elements of the periodic table.
Compare Osmium with all Group 8 elements
Compare Osmium with all Period 6 elements
Compare Osmium with all Transition Metal elements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Find the answers to the most frequently asked questions about Osmium